Spotify SQL Analysis & Query Optimisation
- This project focused on analysing Spotify track data using advanced SQL techniques. The goal was to clean, query, and optimise a denormalised dataset to surface insights around artist performance, track engagement, and streaming platforms.
- Key skills applied: SQL (CTEs, window functions, subqueries, indexing), query optimisation, analytical thinking.

Approach & Highlights
| Focus Area | Action Taken | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Data Understanding | Explored 20+ track attributes including streams, views, tempo, and energy | Built strong dataset familiarity to support deeper analysis |
| Data Querying | Wrote and categorised 15+ queries (basic to advanced) | Extracted key insights on artist activity, album trends, and track metrics |
| Insight Generation | Used groupings, filters, and aggregations across dimensions | Identified top-streamed tracks, most energetic songs, and user engagement |
| Advanced SQL Logic | Applied CTEs and window functions | Ranked top 3 viewed tracks per artist and calculated dynamic metrics |
| Query Optimisation | Used EXPLAIN ANALYSE, indexing, and subquery review | Improved query performance and reduced execution time |
Dashboard
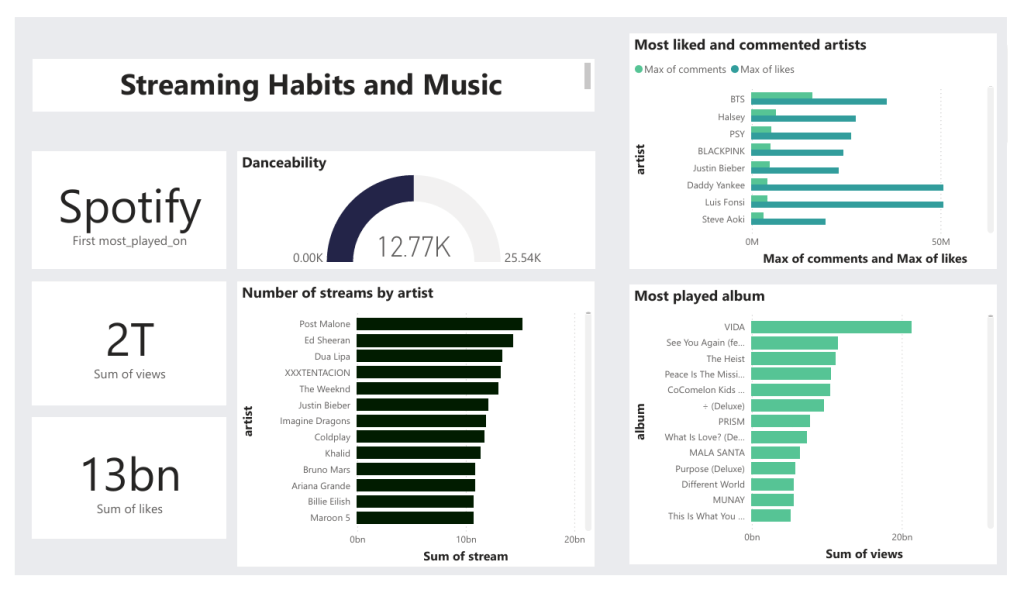
Project Steps
-- create table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS spotify;
CREATE TABLE spotify (
artist VARCHAR(255),
track VARCHAR(255),
album VARCHAR(255),
album_type VARCHAR(50),
danceability FLOAT,
energy FLOAT,
loudness FLOAT,
speechiness FLOAT,
acousticness FLOAT,
instrumentalness FLOAT,
liveness FLOAT,
valence FLOAT,
tempo FLOAT,
duration_min FLOAT,
title VARCHAR(255),
channel VARCHAR(255),
views FLOAT,
likes BIGINT,
comments BIGINT,
licensed BOOLEAN,
official_video BOOLEAN,
stream BIGINT,
energy_liveness FLOAT,
most_played_on VARCHAR(50)
);
1. Data Exploration
Before diving into SQL, it’s important to understand the dataset thoroughly. The dataset contains attributes such as:
Artist: The performer of the track.Track: The name of the song.Album: The album to which the track belongs.Album_type: The type of album (e.g., single or album).- Various metrics such as
danceability,energy,loudness,tempo, and more.
2. Querying the Data
After the data is inserted, various SQL queries can be written to explore and analyze the data.
Easy Queries: Simple data retrieval, filtering, and basic aggregations.
Medium Queries: More complex queries involving grouping, aggregation functions, and joins.
Advanced Queries: Nested subqueries, window functions, CTEs, and performance optimization.
3. Query Optimization
In advanced stages, the focus shifts to improving query performance. Some optimization strategies include:
- Indexing: Adding indexes on frequently queried columns.
Query Execution Plan: Using EXPLAIN ANALYZE to review and refine query performance
SQL Statements
1. Retrieve the names of all tracks that have more than 1 billion streams.
SELECT * FROM spotify
WHERE stream > 1000000000;
2. List all albums along with their respective artists.
SELECT
DISTINCT album,artist
FROM spotify
ORDER BY 1;
SELECT
DISTINCT album
FROM spotify
ORDER BY 1;
3. Get the total number of comments for tracks where licensed = TRUE.
SELECT
SUM(comments) AS total_comments
FROM spotify
WHERE licensed = 'true';
4. Find all tracks that belong to the album type single.
SELECT * FROM spotify
WHERE album_type = 'single';
5. Count the total number of tracks by each artist.
SELECT
artist,
COUNT(*) as total_no_songs
FROM spotify
GROUP BY artist
ORDER BY 2 DESC;
Medium Level
6. Calculate the average danceability of tracks in each album.
SELECT
album,
avg(danceability) as avg_danceability
FROM spotify
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 2 DESC;
7. Find the top 5 tracks with the highest energy values.
SELECT
track,
MAX(energy)
FROM spotify
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 2 DESC
LIMIT 5;
8. List all tracks along with their views and likes where official_video = TRUE.
SELECT
track,
SUM(views) AS total_views,
SUM(likes) AS total_likes
FROM spotify
WHERE official_video = 'true'
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 2 DESC
LIMIT 5;
9. For each album, calculate the total views of all associated tracks.
SELECT
album,
track,
SUM(VIEWS)
FROM spotify
GROUP BY 1,2
ORDER BY 3 DESC;
10. Retrieve the track names that have been streamed on Spotify more than YouTube.
SELECT * FROM
(SELECT
track,
-- most_played_on,
COALESCE(SUM(CASE WHEN most_played_on = 'Youtube' THEN stream END),0) AS streamed_on_youtube,
COALESCE(SUM(CASE WHEN most_played_on = 'Spotify' THEN stream END),0) AS streamed_on_spotify
FROM spotify
GROUP BY 1
) AS T1
WHERE
streamed_on_spotify > streamed_on_youtube
AND
streamed_on_youtube <> 0;
Advanced Level
11. Find the top 3 most-viewed tracks for each artist using window functions.
WITH ranking_artist
AS
(SELECT
artist,
track,
SUM(views) as total_view,
DENSE_RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY artist ORDER BY SUM(views)DESC) as rank
FROM spotify
GROUP BY 1,2
ORDER BY 1,3 DESC)
SELECT * FROM ranking_artist
WHERE rank <= 3;
12. Write a query to find tracks where the liveness score is above the average.
SELECT
track,
artist,
liveness
FROM spotify
WHERE liveness > (SELECT AVG(liveness) FROM spotify);
13. Use a WITH clause to calculate the difference between the highest and lowest energy values for tracks in each album.
WITH cte
AS
(SELECT
album,
MAX(energy) as highest_energy,
MIN(energy) as lowest_energery
FROM spotify
GROUP BY 1
)
SELECT
album,
highest_energy - lowest_energery as energy_diff
FROM cte
ORDER BY 2 DESC
Dashboard

Results
Analysed a denormalised Spotify dataset using advanced SQL techniques to surface key insights across artists, tracks, and platforms.
Key skills: CTEs, window functions, performance tuning, query optimisation
Results:
- Identified top 3 viewed tracks per artist
- Compared stream counts between Spotify and YouTube
- Highlighted high-liveness tracks and energy trends
- Improved query performance with indexing and EXPLAIN plans
From exploratory queries to optimised insights — this project demonstrates SQL depth and data storytelling with real-world impact.
